Published: Oct 10, 2024
Generative AI solutions for Automated Speech Recognition (ASR)
Executive summary
Automated Speech Recognition (ASR) is a common tool used by many businesses to ensure that customer conversations are captured and retained for customer service, legal, and compliance purposes. But linguistic factors can create challenges to ensuring the accurate transcription of conversations, particularly in regions as linguistically diverse as Southeast Asia.
Based on our experience, most AI solutions have challenges in interpreting our local accented speech which often contains a mix of borrowed words from different languages and dialects, idiosyncratic syntax and grammar as well as references to local places.
In this article, we explore the immense potential of ASR to revolutionise business operations, empower growth, and drive unparalleled conversational understanding. Additionally, we will address the current challenges in ASR capabilities, especially in an ASEAN context.
Challenges with ASR capability in an ASEAN context
Automated Speech Recognition (ASR) is a technology that converts spoken language into written text. While ASR technology has been around for some time, several challenges persist, particularly in the ASEAN context:
- Diverse linguistic landscape: The ASEAN region is rich in cultural and linguistic diversity. With multiple languages, accents, and dialects spoken across countries, developing an ASR system that accurately recognises and transcribes all variations presents a considerable challenge.
- Code-switching and creole languages: Many ASEAN countries have a culture of code-switching, where individuals switch between languages in a single conversation. Additionally, the presence of creole languages further complicates ASR accuracy, as these languages often lack standardised grammatical rules and structures.
- Acoustic environment variability: The ASEAN region encompasses diverse acoustic environments, including bustling urban centres and remote rural areas. Background noise, varying speech volumes, and microphone quality can impact ASR performance, requiring robust adaptation techniques.
- Low-resource languages: Some languages in the ASEAN region may have limited data available for training ASR models. The scarcity of training data for low-resource languages hinders the development of highly accurate and robust ASR systems for these languages.
- Accents and pronunciation: Different accents within a single language can lead to misinterpretations by ASR systems. Pronunciation variations can also pose challenges, especially for ASR models designed primarily for standardised speech.
Understanding NCS’ ASR capability and Generative AI
NCS’ very own ASR product, Ins8.ai, is an advanced hyperlocal large vocabulary continuous speech recognition (LVCSR) product developed by the NCS Ins8.ai product team and NCS NEXT Gen Tech teams. It was trained using local call centre data on multiple ASEAN languages and excels in handling accents, dialects, and creole languages, making it ideal for Asia. The core technology is a deep neural network architected and fine-tuned by the Ins8.ai team to ensure exceptional accuracy for spoken creole languages in Asia, such as Singlish. Ins8.ai overcomes the barriers from accents and extended vocabularies that can be challenging for traditional ASR technologies.
Comparison with open-source ASRs
In our comprehensive comparison between the NCS Ins8.ai product and Open AI’s Whisper (ASR system trained on 680,000 hours of audio datasets collected from the web, two-thirds of which are in English), the results clearly demonstrated Ins8.ai’s superiority. Ins8.ai outperformed, producing the lowest word error rate (WER) despite maintaining a small model size (just one-sixth that of Open AI’s Whisper medium model) for typical call centre conversations in Singlish while running at a much higher speed of transcription (Figure 1).
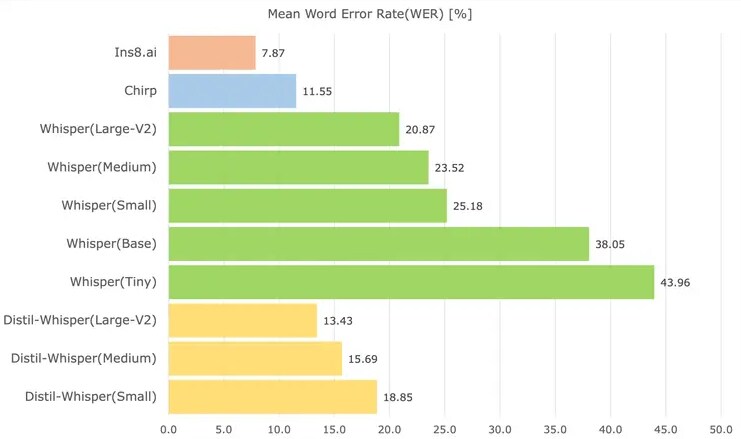
Figure 1. Comparison of NCS Ins8.ai and OpenAI Whisper – Transcription of 150 mins of speech
In a recent implementation with a 250-strong call centre in Singapore, our ASR was applied successfully to live speech-to-text transcription for Singlish, with an accuracy rate of 95% with the ability to interpret Singlish terms like “shiok”, “can-can” and “Wah-low” as well as local places in Singapore. This is in line with the statistics above and compares favourably to out-of-the-box STT which generally has an accuracy rate of 70-80% for Singlish.
Beyond call centres, this capability can also be applied to other use cases, such as:
- Financial services – Transcribe financial consultations (between Banking Relationship Managers or Insurance Financial Advisors and their customers), conversations involving the execution of transactions
- Healthcare – Automate capture of interactions between doctors and patients, or even amongst multiple doctors treating a patient
- Investigations – Transcribe conversations between investigation officers and suspects, as well as calls made by the suspect to accomplices.
Our dedication to developing cutting-edge technology has led to Ins8.ai’s unparalleled performance, making it the clear choice for anyone seeking industry-leading automatic speech recognition capabilities.